Culex plectoporpe Root, 1927
Culex plectoporpe Root, 1927
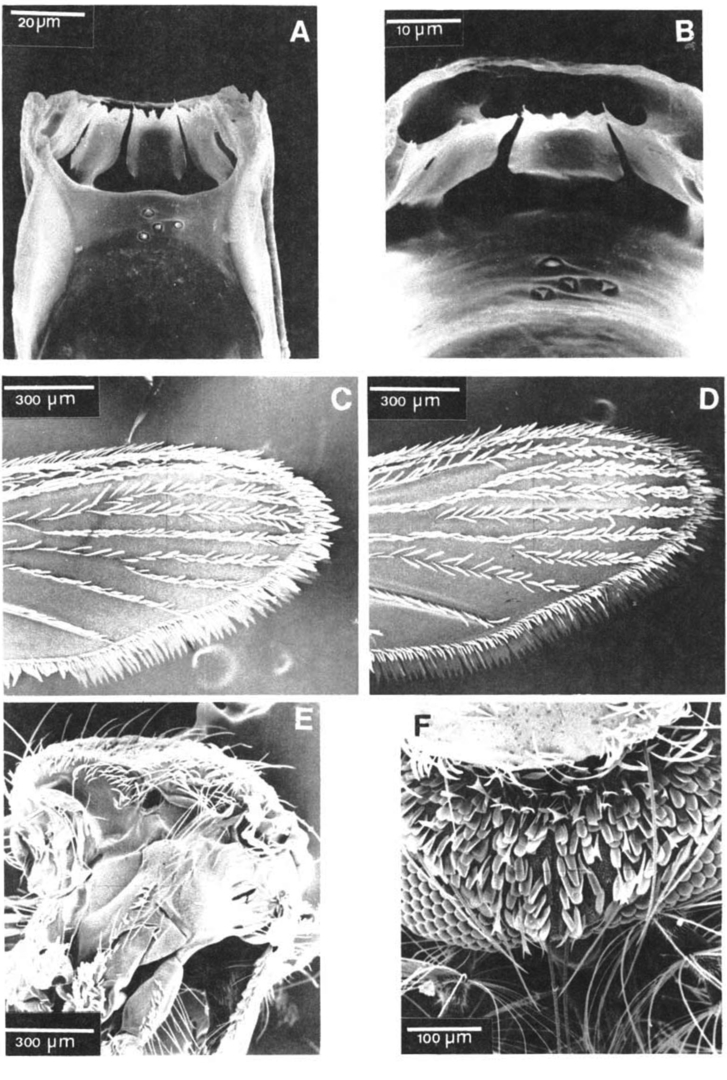
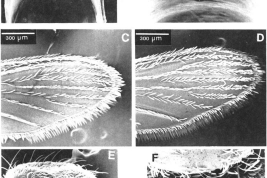
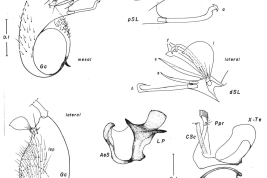
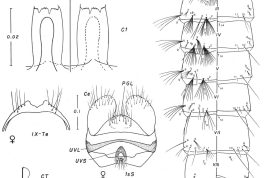
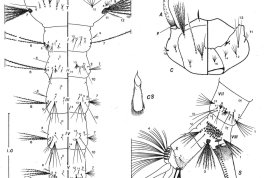
Adults of Culex plectoporpe. Female: A. Dorsal aspect of cibarial armature; B. Detail of figure A focusing the cibarial teeth; C. Dorsal aspect of distal right wing scaling; D. Ventral aspect of distal right wing scaling; E. Aspect of lateral right side of thorax; Male: F. Dorsal aspect of head showing forked and falcate scales (Photo: Foraytini & Mureb-Sallum, 1987).
 Geographic distribution
Geographic distribution
Distribution
Record
- Argentina
- Chaco
- Corrientes
- Formosa
- Misiones
Other distribution
Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, French Guiana, Panama.
- Sin registros/no records .
"Not reported from Argentina by Knight & Stone (1977)." (Mitchell & Darsie, 1985).
The species was found breeding mainly in ground water in manmade environments, following the modifications of the primitive environment. Breeding places include artificial ditches, ponds and even small pools on open ground, associated with land vegetation such as molasses grass. Immature stages were found in biotic sympatry with Culex oedipus and Culex rabelloi. Adults were collected near human settlements, sometimes indoors. Thus, the species was found inside villages in urban areas.
- KNIGHT, K. L., STONE, A. 1977. A catalog of the mosquitoes of the world (Diptera: Culicidae), 2nd ed. Thomas Say Foundation, Entomological Society of American 6: 1-611.
- SIRIVANAKARN, S., JAKOB, W. L. 1981. Notes on the distribution of Culex (Melanoconion) mosquitoes in northeastern Argentina (Diptera: Culicidae). Mosquito Systematics 13 (2): 195-200.
- MITCHELL, C. J., DARSIE, R. F. JR. 1985. Mosquitoes of Argentina. Part II. Geographic distribution and bibliography (Diptera, Culicidae). Mosquito Systematics 17 (4): 279-362.
- FORATTINI, O.P., MUREB-SALLUM, M.A. 1987. Studies on some species of Culex (Melanoconion), with the description of a new one from southern Brazil (Diptera: Culicidae). Revista da Saúde Pública, São Paulo 21:123-156.
- CAMPOS, R. E., MACIÁ, A. 1998. Culicidae. Cap. 28. En Morrone, J. J. & Coscarón, S. (Eds.) Biodiversidad de Artrópodos Argentinos: Una pespectiva biotaxonómica. (pp. 291-303). La Plata, Buenos Aires, Argentina: Ediciones Sur.
- ROSSI, G. C. 2015. Annotated checklist, distribution, and taxonomic bibliography of the mosquitoes (Insecta: Diptera: Culicidae) of Argentina. Check List 11 (4): 1712.
- BANGHER, D. N. 2020. Revisión sistemática de Culex (Melanoconion) Theobald (Diptera: Culicidae) en Argentina. Tesis Doctoral. Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales y Agrimensura, Universidad Nacional del Nordeste, Corrientes, Argentina.
- HOYOS, C. B., MONZÓN, C. M. 2021. Description of the mosquito fauna (Diptera culicidae) in the Department of Formosa, Province of Formosa. Argentine Republic. South Florida Journal of Development 2 (3): 4123-4129.