Geographic distribution
Geographic distribution
Distribution
No economic damages registered
- Argentina
- Misiones
Other distribution
BRAZIL
Paraná, Santa Catarina, Río Grande do Sul
PARAGUAY
Itapúa, San Pedro
Paraná, Santa Catarina, Río Grande do Sul
PARAGUAY
Itapúa, San Pedro
- Cyphus luridus Boheman 1840: 144
- Neocyphus luridus : Dalla Torre, Emden & Emden 1936: 9
- Cyphus gibber luridus : Kuschel 1958: 794
- Cyrtomon luridus : Lanteri 1990a: 396
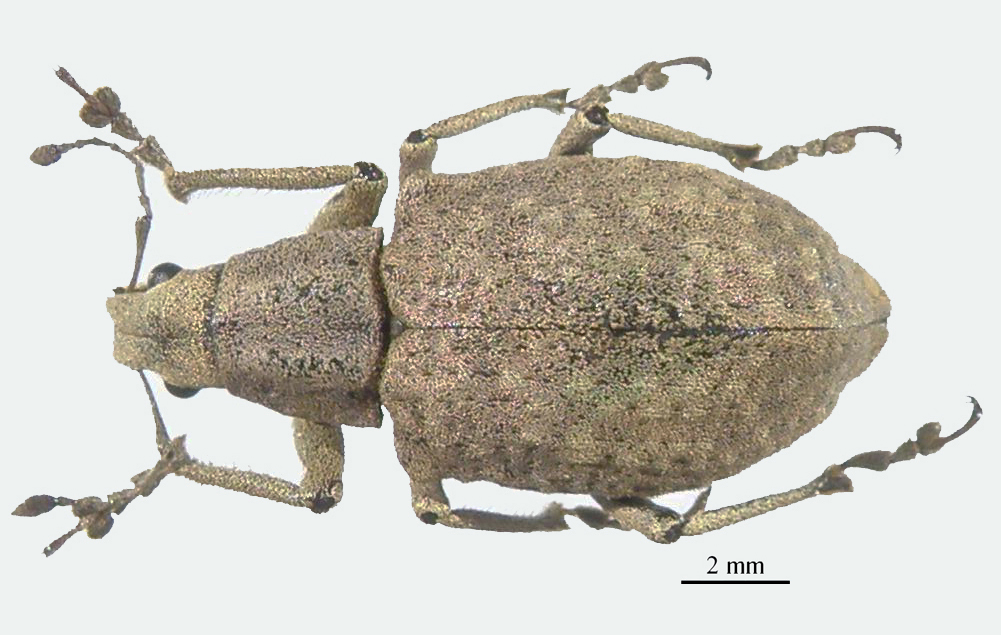
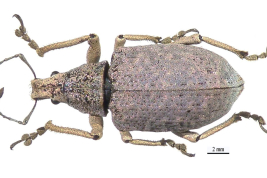
C. luridus distinguished from C. inhalatus because the vestiture is pinkish or grey, and always lighter on head, venter and legs; the sides of the pronotum are less curved than in the other species, and the elytra more rugose, with supernumerary striae always distinct.
Mouthparts of this species were described in Díaz et al. (1990a b) and characters of vestiture in Coscarón et al. (1991).
A key to species of Cyrtomon is provided in Lanteri (1990a) and Lanteri & del Río (2016).
Microctonus sp (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) is a parasitoid of C. luridus that has been investigated for its biological control in Brazil (Tironi et al. 2004).
Mouthparts of this species were described in Díaz et al. (1990a b) and characters of vestiture in Coscarón et al. (1991).
A key to species of Cyrtomon is provided in Lanteri (1990a) and Lanteri & del Río (2016).
Microctonus sp (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) is a parasitoid of C. luridus that has been investigated for its biological control in Brazil (Tironi et al. 2004).
Solanum viarum Dunal in Misiones, Argentina (Lanteri et al. 2002a); Solanum mauritianum Scopoli, Cestrum intermedium Sendt. and Duboisia sp (Solanaceae) in Paraná, Brazil (Tironi et al. 2005). Duboisia sp is a medicinal plant introduced in Brazil from Australia. The weevil is adapted to this plant and the larvae feed on the roots causing 100% damage in Arapongas, Paraná state (Tironi et al. 2005). It is also associated with Eucalyptus spp (Myrtaceae) in São Paulo (Silva et al. 1968).
Associated with the vegetation of the Atlantic and Paranaense forests.
Associated with the vegetation of the Atlantic and Paranaense forests.
- BOHEMAN C.H. 1840. In: Schoenherr, C.J. Genera et species curculionidum cum synonymia hujus familiae. Roret, Paris; Fleischer, Lipsiae. Vol. 6, pt.1, pp. 1-474.
- DALLA TORRE K.W. ET AL. 1936. Coleopterorum Catalogus. Junk, ´s-Gravenhage. Pars 147, Curculionidae: Brachyderinae I, vol. 27, pp. 1-132.
- KUSCHEL G. 1958. Neotropische Rüsselkäfer aus dem Museum G. Frey (Col. Curcul.). Entomologischen Arbeiten aus dem Museum G Frey 9(3): 750-798, illus.
- SILVA A.G. ET AL. 1968. Quarto Catálogo dos insetos que vivem nas plantas do Brasil, seus parasitos e predadores. Ministerio da Agricultura, Departamento de Defesa e Inspecão Agropecuaria, Serviço de Defesa Sanitaria Vegetal, Laboratorio Central de Patología Vegetal. Río de Janeiro, GB, Brasil, 622 pp.
- DÍAZ N.B. ET AL. 1990a. Importancia taxonómica de las piezas bucales en la tribu Naupactini. I. Género Cyrtomon Schoenherr y taxa afines (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Revista Brasileira de Entomologia 34(4): 861-876.
- LANTERI A.A. 1990a. Revisión sistemática del género Cyrtomon Schönherr (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Revista Brasileira de Entomología 34(2): 387-402.
- DÍAZ N.B. ET AL. 1990b. Importancia taxonómica de las piezas bucales en la tribu Naupactini. II. Las especies del género Cyrtomon (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Neotrópica 36(96): 93-99.
- COSCARON M.C. ET AL. 1991. Importancia taxonómica del revestimiento tegumentario en la tribu Naupactini I. Género Cyrtomon y taxa afines (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Neotrópica 37(97): 31-54.
- LANTERI A.A. ET AL. 2002a. Gorgojos de la Argentina y sus plantas huéspedes. Tomo I: Apionidae y Curculionidae. Publicación Especial de la Sociedad Entomológica Argentina Nº 1, 98 pp.
- TIRONI P. ET AL. 2004. Biology of Microctonus sp. (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), a parasitoid of Cyrtomon luridus Boh. (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Scientia Agricola, Piracicaba 61(5): 538-541.
- TIRONI P. ET AL. 2005. Populations dynamics of Cyrtomon luridus Boheman (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) on Duboisea sp (Solanaceae) in Brazil. Scientia Agricola 62(5). http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0103-90162005000500011
- LANTERI A.A. & DEL RÍO M.G. 2016. Taxonomy and cladistics of the group of genera related to Cyrtomon Schöenherr (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Naupactini). Revista de la Sociedad Entomológica Argentina 75(1-2): 55-77.