Culex educator Dyar and Knab, 1906
Culex educator Dyar and Knab, 1906
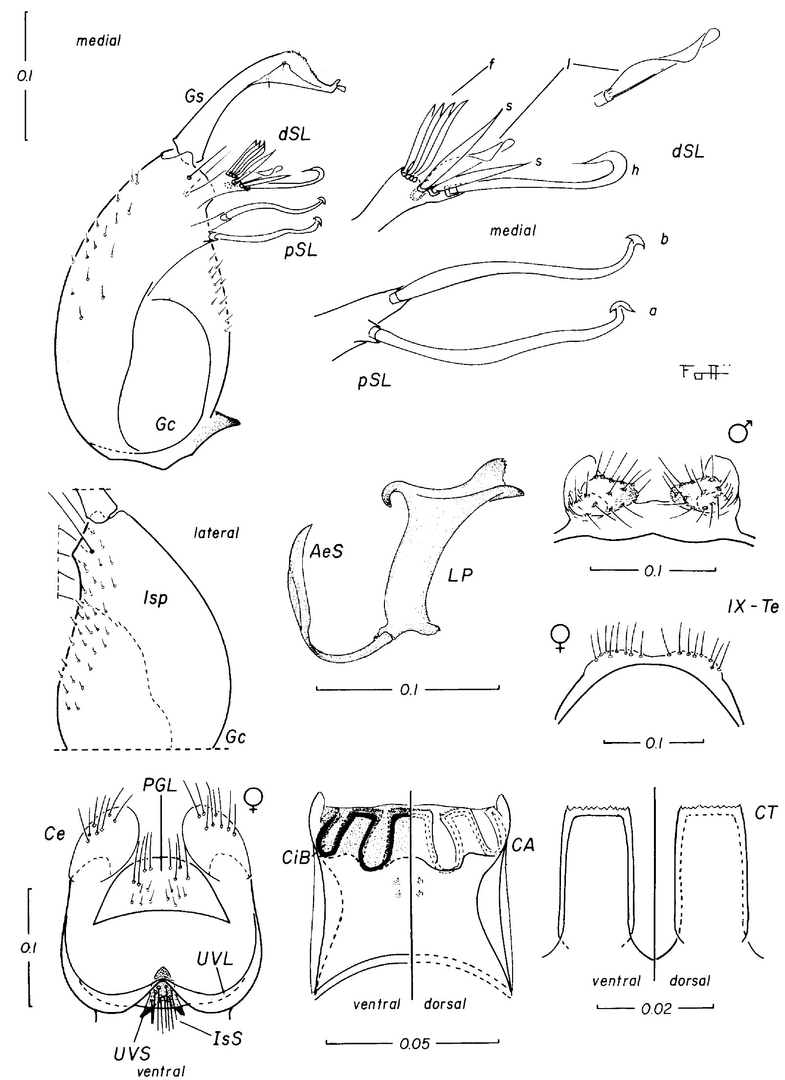
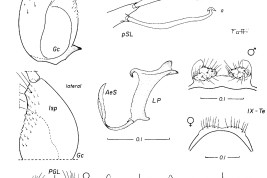
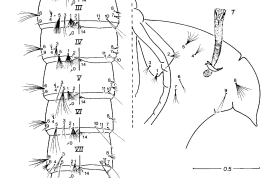
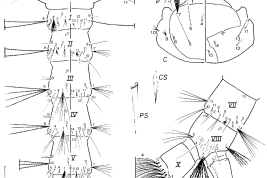
Female and male genitalia and cibarial armature of Culex educator. a = seta a of pSL; AeS = aedeagal sclerite; b = seta b of pSL; CA = cibarial armature; Ce = cercus; CiB = cibarial bar; CT = cibarial tooth; dSL = distal division of subapical lobe; f = foliform seta of dSL; Gc = gonocoxite; Gs = gonostylus; h = hooked seta of dSL; IsS = insular seta; l = leaf seta of dSL; LP = lateral plate; lsp = lateral setal patch; PGL = postgenital lobe; pSL = proximal division of subapical lobe; s = saberlike seta of dSL; UVL = upper vaginal lip; UVS = upper vaginal sclerite; IX-Te = tergum IX (Photo: Forattini & Sallum, 1993a).
 Geographic distribution
Geographic distribution
Distribution
Record
- Argentina
- Chaco
- Córdoba
- Corrientes
- Entre Ríos
- Formosa
- Misiones
Other distribution
Belize, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, El Salvador, French Guiana, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Puerto Rico, Suriname, Venezuela
- aneles Dyar and Ludlow
- apeteticus Howard, Dyar, and Knab
- keenani Galindo and Méndez
Disease relations: The species has been found naturally infected with the Bunyamwera virus in Formosa Province (Gallardo et al., 2019).
Immature stages have been collected in the following types of habitats: artificial ponds and small ground pools in a domestic area, marshy canal, small ground pools in a dry stream bed in a cultivated area, swamp margin in the partial forest, small ground pools in secondary growth, small ground pools along a watercourse, swamp interior, lakes, lake margins, lake margins in the forest, ponds in grazing areas, the margin of a swampy area at the edge of a river in a grazing area. They were taken in full sun, partial or deep shade in stagnant or slow-moving water. The water is clear or turbid, permanent, semipermanent, or temporary. Some breeding places have no vegetation; others have very little or abundant algae, and grassy, herbaceous, floating (Pistia, Eichhernia, Lemna), and submerged (Elodea) vegetation.
Females and larvae were registered throughout the year in Chaco Province, Argentina.
Females and larvae were registered throughout the year in Chaco Province, Argentina.
- DURET, J. P. 1953a. Las especies argentinas de Culex (Melanoconion) (Diptera-Culicidae). I. Introduccion. Revista de la Sociedad Entomológica Argentina 16 (3): 67-76.
- DURET, J. P. 1953b. Notas sobre Culex argentinos. (Diptera-Culicidae). Revista de la Sanidad Militar Argentina 52 (2): 272-278.
- DURET, J. P. 1954c. Las especies argentinas de Culex (Melanoconion) (Diptera: Culicidae). VII. Descripción de los Culex (Melanoconion) argentinos. Revista de la Sociedad Entomológica Argentina 16(4): 99-121.
- CASTRO, M., GARCÍA, M., BRESSANELLO, M. D. 1959 (1960). Diptera Culicidae Culicinae, p. 547-562. En: J. F. R. Bejarano, E. Del Ponte and R. N. Orfila (ed.), Primeras Jornadas Entomoepidemiológicas Argentinas 2, Buenos Aires.
- KNIGHT, K. L., STONE, A. 1977. A catalog of the mosquitoes of the world (Diptera: Culicidae), 2nd ed. Thomas Say Foundation, Entomological Society of American 6: 1-611.
- MITCHELL, C. J., DARSIE, R. F. JR. 1985. Mosquitoes of Argentina. Part II. Geographic distribution and bibliography (Diptera, Culicidae). Mosquito Systematics 17 (4): 279-362.
- FORATTINI, O.P., MUREB-SALLUM, M.A. 1993a. Taxonomic study of some species of the educator group of Culex (Melanoconion) (Diptera: Culicidae). Mosquito Systematics 25(2):89-109.
- CAMPOS, R. E., MACIÁ, A. 1998. Culicidae. Cap. 28. En Morrone, J. J. & Coscarón, S. (Eds.) Biodiversidad de Artrópodos Argentinos: Una pespectiva biotaxonómica. (pp. 291-303). La Plata, Buenos Aires, Argentina: Ediciones Sur.
- VISINTÍN, A. M., LAURITO, M., STEIN, M., RAMÍREZ, P., MOLINA, G., LORENZO, P. R., ALMIRÓN, W. R. 2010. Two new mosquito species and six new provincial records in Argentina. Journal of the American Mosquito Control Association 26 (1): 91-94.
- ROSSI, G. C. 2015. Annotated checklist, distribution, and taxonomic bibliography of the mosquitoes (Insecta: Diptera: Culicidae) of Argentina. Check List 11 (4): 1712.
- BANGHER, D. N. 2020. Revisión sistemática de Culex (Melanoconion) Theobald (Diptera: Culicidae) en Argentina. Tesis Doctoral. Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales y Agrimensura, Universidad Nacional del Nordeste, Corrientes, Argentina.