Geographic distribution
Geographic distribution
Distribution
Record
- Argentina
- Catamarca
- Chaco
- Córdoba
- Corrientes
- Formosa
- Jujuy
- La Pampa
- La Rioja
- Mendoza
- Misiones
- Salta
- San Juan
- San Luis
- Santa Fe
- Santiago del Estero
- Tucumán
Other distribution
Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, French Guiana, Paraguay, Trinidad and Tobago, Venezuela
- lindneri Martini
- uriartei Shannon and Del Ponte
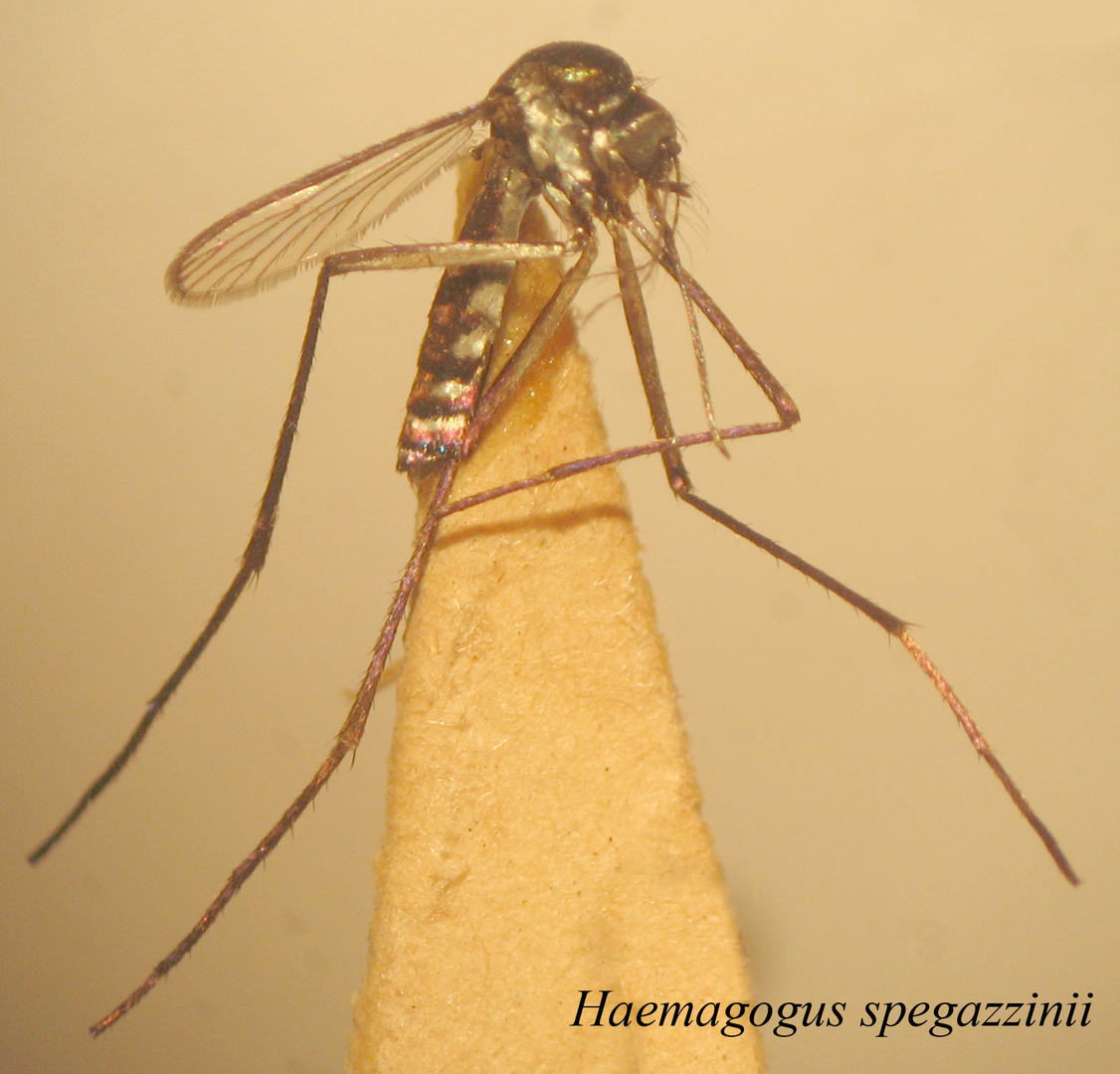
"The type locality for this species is in Jujuy Province, locality not specified (Knight & Stone, 1977). Before the monograph of Arnell (1973), this species and its subspecies, falco (now a synonym of janthinomys) were thought to be extensively distributed in Central and South America. Under the present concept, spegazzini (s. str.) is confined to eastern and southern Brazil, eastern Bolivia, Paraguay, and northern Argentina. This species extends farther south in Argentina than any other Haemagogus. A synonym of spegazzini, Haemagogus uriartei Shannon & Del Ponte, was the name used by Duret (1950c, 1951b, 1952) and Castro et al. 1959 (1960) for this species. It was synonymized under spegazzini by Martínez et al. (1961a)" (Mitchell & Darsie, 1985).
Disease relations: Haemagogus spegazzini effectively transmits the Mayaro virus (Muñoz & Navarro, 2012).
Disease relations: Haemagogus spegazzini effectively transmits the Mayaro virus (Muñoz & Navarro, 2012).
Larvae have been collected in water bodies of natural environments such as holes in trees and rocks (Lane, 1953). In Argentina, the species has been reported breeding in tree holes in Salta, Córdoba, Chaco (Campos & Gleiser, 2016; Stein et al., 2012), and La Pampa (Obholz et al., 2020) provinces. In the latter study, Prosopis caldenia has been recorded as a new host plant to Haemagogus spegazzinii breeding sites (Obholz et al., 2020), as well as Prosopis nigra (Alvarez et al., 2024). Females do not have anthropophilic behavior and have been captured during daylight hours (Campos & Gleiser, 2016; Díaz Nieto et al., 2020).
- DURET, J. P. 1951b. Contribución al conocimiento de la distribución geográfica de los culicidos Argentinos. (Diptera-Culicidae). Parte III. Revista de la Sanidad Militar Argentina 50 (2): 211-117
- DURET, J. P. 1952. Nueva contribución al conocimiento de la distribución geográfica de los culicidos argentinos. Revista de la Sanidad Militar Argentina 51: 345-356.
- MANSO SOTO, A. E., MARTÍNEZ, A., PROSEN, A. F. 1953. Distribución geográfica de Haemagogus spp, y Aedes (Gualteria) leucocelaenus en Argentina y Bolivia según materiales de M.E.P.R.A. Misión de Estudios de Patología Regional Argentina 24 (83-89): 33-41,
- MARTÍNEZ, A., PROSEN, A. F. 1953c. Nuevos culícidos para las entomofaunas de Argentina, Bolivia y Paraguay. Misión Estud, Patol. Reg. Arg, 24 (83-84): 27-32, también En: J. F. R. BEJARANO, E. DEL PONTE y R. N. ORFILA, R. N. (eds.) 1959 (1960). Primeras Jornadas Entomoepidemiológicas Argentinas 2: 603-607.
- BEJARANO, J., DURET, J. 1954. Hallazgo de Haemagogus uriartei en la ciudad de San Luis. Revista de la Sanidad Militar Argentina 53 (3): 353-354.
- DEL PONTE, E. 1958. Manual de Entomología Médica y Veterinaria Argentinas. Libreria Colegio, Buenos Aires, 349 p.
- ALVARADO, C. A., COLL, H. A., UMANA, A. C., HEREDIA, R. L. 1959 (1960). Contribución al conocimiento de la biología de vectores selváticos de fiebre amarilla en el noroeste argentino. Primeras Jornadas Entomoepidemiológicas Argentinas 1:183-200.
- CASTRO, M., GARCÍA, M., BRESSANELLO, M. D. 1959 (1960). Diptera Culicidae Culicinae, p. 547-562. En: J. F. R. Bejarano, E. Del Ponte and R. N. Orfila (ed.), Primeras Jornadas Entomoepidemiológicas Argentinas 2, Buenos Aires.
- BIANCHINI, N., BIANCHINI, J. P., ASTEGIANO, M. 1965 (1967). Especies de mosquitos de la provincia de Córdoba (Diptera, Culicidae). Segundas Jornadas Entomoepidemiológicas Argentinas 2: 191-194.
- BELKIN, J. N., SCHICK, R. X., HEINEMANN, S. 1968. Mosquito studies (Diptera, Culicidae). XI. Mosquitoes originally described from Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, Paraguay, Peru, and Uruguay. Contribution of the American Entomological Institute 4 (1): 9-29.
- CARCAVALLO, R. U., MARTÍNEZ, A. 1968a. Entomoepidemiología de la República Argentina. Capítulo III. Fiebre amarilla, vectores y cadena epidemiológica. Commun. Cient. Jta. Invest. Cient. Fuerzas Arm. Arg. 13(1): 1-144.
- FORATTINI, O. P., RABELLO, E. X., COTRIM, M. D. 1970. Catalago das colecoes entomologicas da Faculdade de Saude Publica da Universidade de São Paulo (l.ª Serie). Culicidae. Revista da Saúde Pública, São Paulo Vol. 4, Serie Monografica 1: 1-100.
- ARNELL, J. H. 1973. Mosquito studies (Diptera, Culicidae) XXXII. A revision of the genus Haemagogus. Contribution of the American Entomological Institute 10(2):1-174.
- KNIGHT, K. L., STONE, A. 1977. A catalog of the mosquitoes of the world (Diptera: Culicidae), 2nd ed. Thomas Say Foundation, Entomological Society of American 6: 1-611.
- HACK, W. H., TORALES, G. J., BAR, M. E., OSCHEROV, B. 1978. Observaciones etologícas sobre culícidos de Corrientes. Revista de la Sociedad Entomológica Argentina 37 (1-4): 137-151.
- MITCHELL, C. J., DARSIE, R. F. JR. 1985. Mosquitoes of Argentina. Part II. Geographic distribution and bibliography (Diptera, Culicidae). Mosquito Systematics 17 (4): 279-362.
- MACIÁ, A. 1995a. Ampliación de la distribución geográfica de Haemagogus spegazzini (Diptera: Culicidae) a la provincia de Mendoza (Argentina). Revista de la Sociedad Entomológica Argentina 54 (1-4): 58.
- CAMPOS, R. E., MACIÁ, A. 1998. Culicidae. Cap. 28. En Morrone, J. J. & Coscarón, S. (Eds.) Biodiversidad de Artrópodos Argentinos: Una pespectiva biotaxonómica. (pp. 291-303). La Plata, Buenos Aires, Argentina: Ediciones Sur.
- MUÑOZ, M., NAVARRO, J. C. 2012. Virus Mayaro: un arbovirus reemergente en Venezuela y Latinoamérica. Biomédica. 32: 286-302.
- STEIN, M., HOYOS, C. B., ORIA, G. I., BANGHER, D., WEINBERG, D., ALMIRÓN, W. R. 2012. New records of mosquito species (Diptera: Culicidae) for the provinces of Chaco and Formosa, Argentina. Journal of the American Mosquito Control Association 28 (4): 307-308.
- ROSSI, G. C. 2015. Annotated checklist, distribution, and taxonomic bibliography of the mosquitoes (Insecta: Diptera: Culicidae) of Argentina. Check List 11 (4): 1712.
- CAMPOS, R. E., GLEISER, R. M. 2016. Mosquitos que crían en microambientes acuáticos naturales. Sec. 3, cap. 11: 119-141. En: BERÓN, C., CAMPOS, R. E., GLEISER, R. M., DÍAZ NIETO, L. M., SALOMÓN, O. D., SCHWEIGMANN, N. Investigaciones sobre mosquitos de Argentina. Universidad Nacional de Mar del Plata, Mar del Plata.
- OBHOLZ, G., DIEZ, F., SAN BLAS, G., ROSSI, G. C. 2020. The austral-most record of the genus Haemagogus Williston (Diptera: Culicidae). Journal of the Brazilian Society of Tropical Medicine 53:e20190222.
- CANO, M. E., MARTÍ, G. A., BALSALOBRE, A., MUTTIS, E., BRUNO, E. A., ROSSI, G. C., MICIELLI, M. V. . 2021. Database of Sabethes and Haemagogus (Diptera: Culicidae) in Argentina: Sylvatic Vectors of the Yellow Fever Virus. Journal of Medical Entomology. DOI: 10.1093/jme/tjab059
- LAURITO, M., AYALA, A. M., ARIAS-BUILES, D. L., ALMIRÓN, W. R. 2021. Improving the DNA barcode library of mosquito species with new identifications and discoveries in north-central Argentina. Journal of Medical Entomology ournal of Medical Entomology doi.org/10.1093/jme/tjab160
- ALVAREZ, C. N., CAMPOS, R. E., STEIN, M. 2024. Phytotelmata in native and exotic plants and their mosquito (Diptera: Culicidae) assemblages: Diversity and first records of plant-mosquito associations in a subtropical region of Argentina. Ecología Austral 34: 496-511. https://doi.org/10.25260/EA.24.34.3.0.2373.