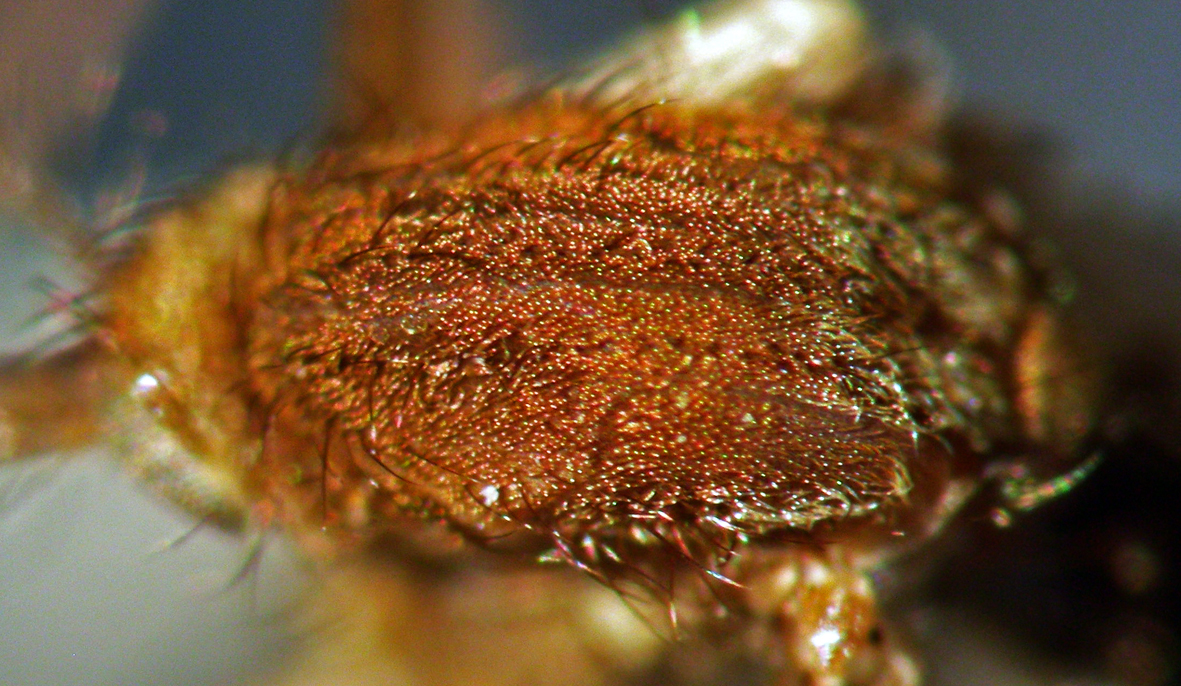
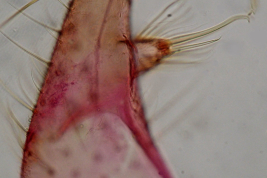
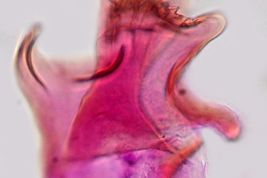
Geographic distribution
Geographic distribution
Distribution
Record
- Argentina
- Catamarca
- Chaco
- Córdoba
- Corrientes
- Formosa
- Jujuy
- La Pampa
- La Rioja
- Misiones
- Salta
- San Juan
- San Luis
- Santa Fe
- Santiago del Estero
- Tucumán
- Uruguay
Other distribution
Brazil, Colombia, Panama, Paraguay, Venezuela
- beauperthuyi Anduze
Type locality: Camp Santa de Salta, Salta Province, Argentina.
Disease relations: females of Culex saltanensis are considered the primary vector of Plasmodium juxtanucleare, which affects chickens
(Consoli and de Oliveira 1994) and are also efficient experimental vectors of Plasmodium cathemerium, another avian parasite (de Oliveira & Castro 1991). The species is susceptible to SLEV and competent for its transmission in laboratory conditions (Beranek et al. 2020).
Disease relations: females of Culex saltanensis are considered the primary vector of Plasmodium juxtanucleare, which affects chickens
(Consoli and de Oliveira 1994) and are also efficient experimental vectors of Plasmodium cathemerium, another avian parasite (de Oliveira & Castro 1991). The species is susceptible to SLEV and competent for its transmission in laboratory conditions (Beranek et al. 2020).
Immature stages have been collected in water accumulated in land depressions and puddles originated by rainfalls or overflowing, between rocks. Larvae also develop in artificial concrete ponds with high sun exposure, and water with a large number of algae and organic matter in suspension (Linares et al. 2016). Larvae were collected from artificial breeding sites like disused tires and pools of water created by excessive urban irrigation (Díaz Nieto et al. 2020). Larvae were found coexisting with Ochlerotatus albifasciatus larvae in natural and artificial breeding sites (Díaz Nieto et al. 2020). Females were captured on humans, occasionally inside houses, and with chicken-baited traps.
- DURET, J. P. 1951a. Contribución al conocimiento de la distribución geográfica de los culicidos argentinos (Diptera-Culicidae). Parte II. Revista de la Sanidad Militar Argentina 50: 64-72.
- DURET, J. P. 1953b. Notas sobre Culex argentinos. (Diptera-Culicidae). Revista de la Sanidad Militar Argentina 52 (2): 272-278.
- CASTRO, M., GARCÍA, M., BRESSANELLO, M. D. 1959 (1960). Diptera Culicidae Culicinae, p. 547-562. En: J. F. R. Bejarano, E. Del Ponte and R. N. Orfila (ed.), Primeras Jornadas Entomoepidemiológicas Argentinas 2, Buenos Aires.
- BRAM, R. A. 1967. Classification of Culex subgenus Culex in the New World (Diptera: Culicidae). Proceedings of the United States National Museum 120 (3557): 1-122
- BELKIN, J. N., SCHICK, R. X., HEINEMANN, S. 1968. Mosquito studies (Diptera, Culicidae). XI. Mosquitoes originally described from Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, Paraguay, Peru, and Uruguay. Contribution of the American Entomological Institute 4 (1): 9-29.
- KNIGHT, K. L., STONE, A. 1977. A catalog of the mosquitoes of the world (Diptera: Culicidae), 2nd ed. Thomas Say Foundation, Entomological Society of American 6: 1-611.
- MITCHELL, C. J., DARSIE, R. F. JR. 1985. Mosquitoes of Argentina. Part II. Geographic distribution and bibliography (Diptera, Culicidae). Mosquito Systematics 17 (4): 279-362.
- CAMPOS, R. E., MACIÁ, A. 1998. Culicidae. Cap. 28. En Morrone, J. J. & Coscarón, S. (Eds.) Biodiversidad de Artrópodos Argentinos: Una pespectiva biotaxonómica. (pp. 291-303). La Plata, Buenos Aires, Argentina: Ediciones Sur.
- VISINTÍN, A. M., LAURITO, M., STEIN, M., RAMÍREZ, P., MOLINA, G., LORENZO, P. R., ALMIRÓN, W. R. 2010. Two new mosquito species and six new provincial records in Argentina. Journal of the American Mosquito Control Association 26 (1): 91-94.
- ROSSI, G. C., MARTÍNEZ, M. 2013. Lista de especies y clave ilustrada para la identificación de larvas de mosquitos (Diptera: Culicidae) halladas criando en recipientes artificiales en Uruguay. Boletín de la Sociedad Zoológica del Uruguay (2ª época) 22 (2): 49-65.
- LAURITO, M., VISINTIN, A. M., LORENZO, P. R., BERRÓN, C. I., DIEZ, N., ALMIRÓN, W. R. 2013b. New records of mosquito species (Diptera: Culicidae) from Catamarca and Santa Fe provinces, Argentina. Revista de la Sociedad Entomológica Argentina 72 (3-4): 215-217.
- ROSSI, G. C. 2015. Annotated checklist, distribution, and taxonomic bibliography of the mosquitoes (Insecta: Diptera: Culicidae) of Argentina. Check List 11 (4): 1712.
- LINARES, M. A., LAURITO, M., VISINTIN, A. M., ROSSI, G. C., STEIN, M., ALMIRÓN, W. R. 2016. New mosquito records (Diptera: Culicidae) from northwestern Argentina. Check List 12 (4): art 1944
- BERANEK, M. 2019. Mosquitos Culex (Diptera: Culicidae) posibles vectores del virus St. Louis Encephalitis (Flavivirus) en ambientes urbanos y rurales de la provincia de Córdoba. Tesis Doctoral. Universidad Nacional de Córdoba, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas, Físicas y Naturales.
- BERANEK, M. D., QUAGLIA, A. I., PERALTA, G. C., FLORES, F. S., STEIN, M., DIAZ, L. A. ALMIRÓN, W. R., CONTIGIANI, M. S. . 2020. Culex interfor and Culex saltanensis (Diptera: Culicidae) are susceptible and competent to transmit St. Louis encephalitis virus (Flavivirus: Flaviviridae) in central Argentina. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and HygieneTrans 1–5.
- BERANEK, M. D., QUAGLIA, A. I., PERALTA, G., FLORES, F. S., STEIN, M., DÍAZ, L. A., ALMIRÓN, W. R., CONTIGIANI, M. 2020. Culex interfor and Culex saltanensis (Diptera: Culicidae) are susceptible and competent to transmit St. Louis encephalitis virus (Flavivirus: Flaviviridae) in central Argentina. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene DOI: 10.1093/trstmh/traa058